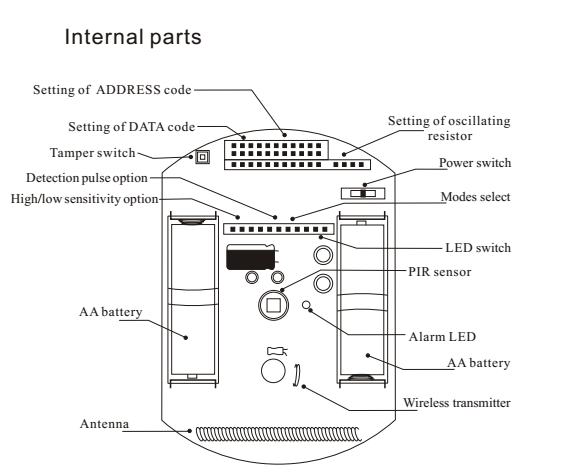
The Difference Between Passive Infrared Detectors and Active Infrared Detectors
Infrared detectors are essential components in modern security systems, helping to safeguard homes, businesses, and other premises. Among the various types of infrared detectors, Passive Infrared Detectors (PIR) and Active Infrared Detectors (AIR) are the most commonly used. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right solution for your security needs.
What Are Passive Infrared Detectors?
Passive infrared detectors are devices that sense infrared radiation emitted by objects, particularly humans and animals, within their field of view. These detectors do not emit any infrared signals; instead, they rely on detecting changes in infrared energy caused by movement.

Key Features of Passive Infrared Detectors:
No Emission: They passively detect infrared radiation, making them energy-efficient.
Wide Applications: Ideal for indoor use, such as home security systems and motion-activated lighting.
Affordable: Generally cost-effective and easy to install.
Sensitivity to Heat: They detect the heat signatures of moving objects.
What Are Active Infrared Detectors?
Active Infrared Detectors function by emitting infrared beams from a transmitter to a receiver. When an object or person crosses the beam, the signal is interrupted, triggering an alarm.
Key Features of Active Infrared Detectors:
Emits Infrared Beams: Actively sends signals to detect intrusions.
Higher Range: Suitable for outdoor use and long-distance coverage.
Accuracy: Less prone to false alarms caused by environmental factors like heat or light changes.
Dual Components: Require both a transmitter and a receiver for operation.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Infrared Detectors
| Feature | Passive Infrared Detectors (PIR) | Active Infrared Detectors (AIR) |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Method | Detects heat signatures | Detects interruption of infrared beams |
| Energy Emission | Passive (no emission) | Active (emits infrared beams) |
| Application | Indoor | Outdoor or perimeter security |
| False Alarm Rate | May be triggered by pets or heat changes | Lower, due to controlled beam interruption |
| Installation | Easy and cost-effective | Requires alignment of transmitter and receiver |
Choosing the Right Infrared Detector for Your Needs
When deciding between Passive Infrared Detectors and Active Infrared Detectors, consider the specific requirements of your security setup:
For indoor areas with minimal environmental interference, PIR detectors are cost-effective and reliable.
For outdoor spaces or areas requiring long-range detection, AIR detectors provide enhanced accuracy and coverage.
Applications of Passive and Active Infrared Detectors
Common Uses of Passive Infrared Detectors:
Motion-activated lighting systems
Indoor home security systems
Automatic door opening mechanisms
Common Uses of Active Infrared Detectors:
Perimeter protection for outdoor security
Industrial safety systems
Vehicle detection in parking lots
Conclusion:
Both Passive Infrared Detectors and Active Infrared Detectors play vital roles in security systems, but their functionality and use cases differ significantly. By understanding their key features and applications, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your security goals. Whether you need reliable indoor motion detection or robust outdoor perimeter protection, there is an infrared detector designed to meet your needs.
Infrared security systems Passive infrared motion detector PIR detector vs. AIR detector Infrared alarm system manufacturers
 简体中文
简体中文